
The emittance of an object quantifies how much light is emitted by it. On the other hand, nuclear shell transitions can emit high energy gamma rays, while nuclear spin transitions emit low energy radio waves. For example, visible light is emitted by the coupling of electronic states in atoms and molecules (then the phenomenon is called fluorescence or phosphorescence). The energy states of the transitions can lead to emissions over a very large range of frequencies. Since energy must be conserved, the energy difference between the two states equals the energy carried off by the photon. The frequency of light emitted is a function of the energy of the transition. In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light.

Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference.
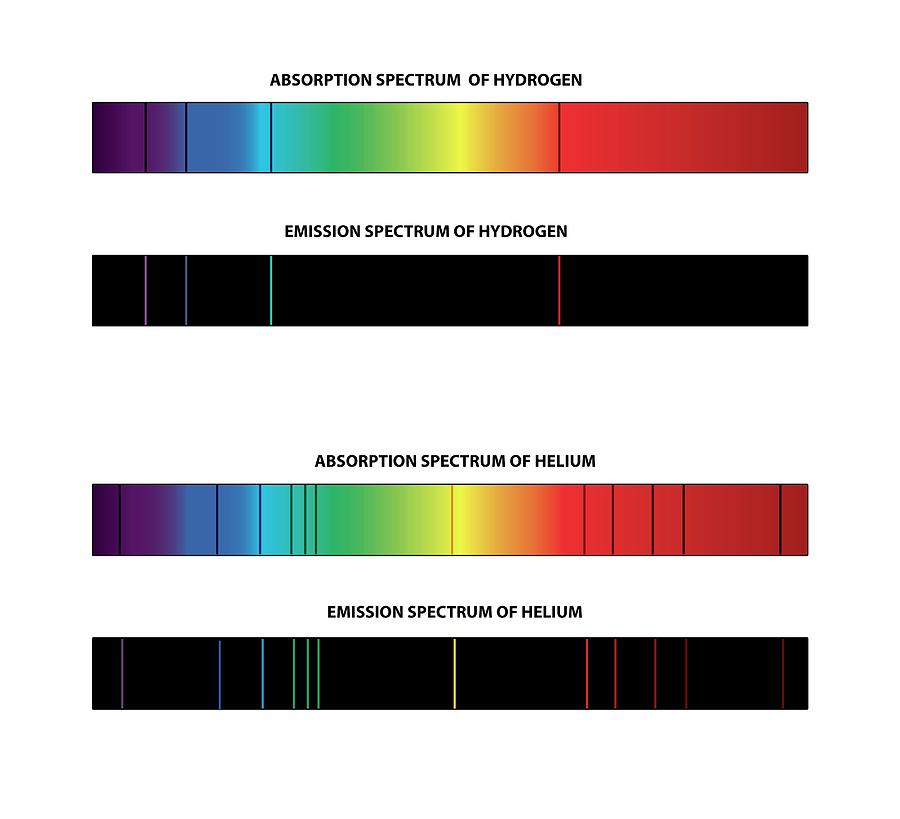
The photon energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy difference between the two states. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. A demonstration of the 589 nm D 2 (left) and 590 nm D 1 (right) emission sodium D lines using a wick with salt water in a flame


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
